Introduction – What Phase-Driven Solar Means for a Starter Kit
Phase-driven solar is a practical pathway to transform a simple solar starter kit into a full home backup without guessing the end goal. You plan, test, and scale in six deliberate steps, prioritizing essential loads during outages while keeping costs and risk in check. This approach gives you real results before big investments, clarity on true capacity needs, and a clear upgrade path.
By following six distinct phases, you’ll craft a scalable, reliable home solar backup that grows with your energy use and budget. The goal is a practical, resilient system that makes sense today—and scales for tomorrow.
Phase 1 – Baseline Assessment: Determine loads, critical circuits, and existing capacity
Inventory current hardware and document performance limits
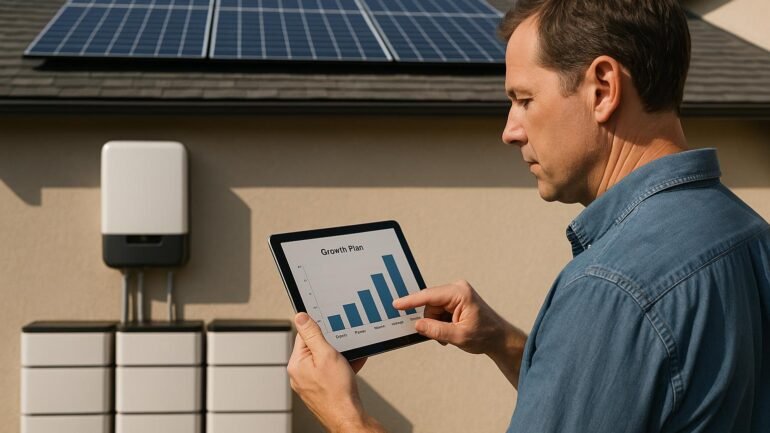
List your inverter/charger, battery bank, and solar array. Record rated capacities, voltage, achievable runtime, and known performance limits. This baseline keeps expectations grounded as you grow.
Establish target backup load and reliability goals
Identify essential loads (refrigeration, lighting, communication, medical or security devices) and set a daily energy target with a safety margin. Use Phase 1 data to guide every future upgrade.
Phase 2 – System Design: Choose panels, inverter, and battery to match growth
Sizing guidance for different backup scenarios (partial vs. full home)
Model several scenarios: partial load backup for critical circuits, or full-home backup for everything. Align panel count, battery capacity, and inverter rating with the chosen target.
Battery chemistry options, safety, and warranty considerations
Compare lead-acid, lithium (LFP, NMC, etc.), and other chemistries. Evaluate safety, thermal management, warranty terms, and expected cycle life to inform choices.
Phase 3 – Core Upgrades: Wiring, safety, permits, and code compliance
Electrical upgrades, grounding, and surge protection
Upgrade wiring where needed, ensure correct grounding, and install surge protection to protect equipment and home.
Inspections and documentation for permits
Prepare plans, drawings, and checklists for permits and inspections. Keep records to streamline approvals and future maintenance.
Phase 4 – Automation & Monitoring: Implement control, monitoring, load shaping
Smart meters, Wi-Fi monitoring, and automatic battery management
Deploy monitoring that tracks state of charge, inverter efficiency, and production. Enable automatic battery control and remote visibility.
Phase 5 – Validation & Testing: Outage drills and performance optimization
Run outage simulations, check inverter ramp rates, verify runtime
Simulate outages, verify ramp rates match expected loads, and confirm runtime targets under various conditions. Use findings to optimize load prioritization and charging strategies.
Phase 6 – Scaling for the Future: Maintenance, budgeting, and rebalancing
Scheduled maintenance, battery health checks, firmware updates
Establish a regular maintenance schedule, monitor battery health, apply firmware updates, and verify safety safeguards remain effective.
Seasonal Alignment: Best times to upgrade and audit across seasons
Align upgrades and audits with seasonal changes in sunlight, temperature, and energy use to keep the system performing reliably year-round.
Risk, Pitfalls, and How to Avoid Them
Be mindful of common missteps: overbuilding too soon, underestimating maintenance, and neglecting safety. Plan, test, document, and pace upgrades to stay in control.
Tools, Resources, and Quick-Start Checklists
Use checklists, supplier references, and calibration guides to stay organized throughout your phase-driven journey.
Closing thoughts
A phase-driven approach reframes the journey from a single upfront purchase into a guided evolution. With six deliberate phases, you’ll size, design, upgrade, automate, test, and finalize a home solar backup that scales with your needs—reducing risk, improving budgeting, and ensuring essential loads stay powered when the grid fails. Start with Phase 1, collect data, and progress confidently toward a robust, whole-home backup that protects your home and peace of mind.