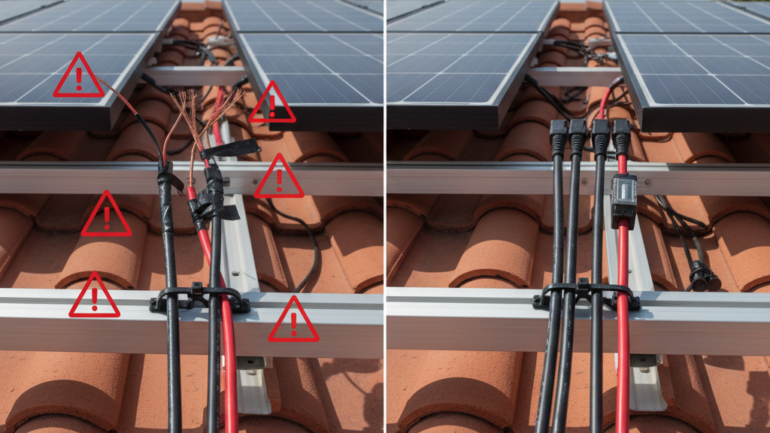
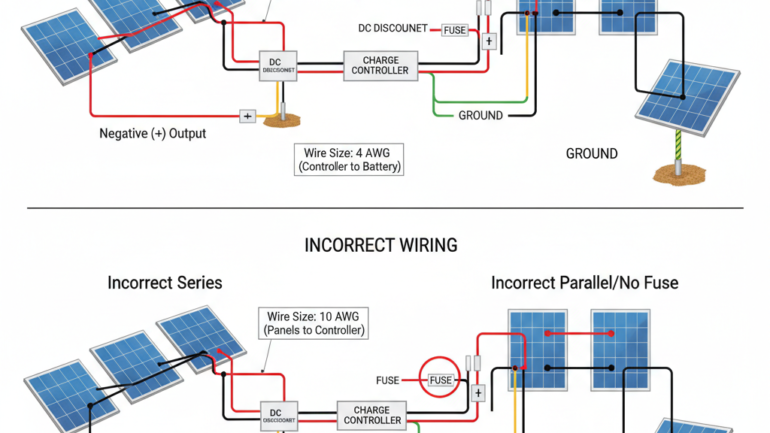
Wiring mistakes can turn your exciting DIY solar project into a costly headache. Furthermore, improper connections create serious safety hazards that could damage equipment or worse. Consequently, understanding common errors helps you build a reliable system from the start. Most importantly, these mistakes are completely preventable with proper knowledge and preparation.
Solar panel wiring forms the backbone of your entire system. Additionally, correct connections ensure maximum power transfer and long-term reliability. However, many beginners rush through this critical step without proper planning. Therefore, taking time to understand proper techniques saves money and prevents dangerous situations.
Understanding Basic Solar Wiring Principles
Before diving into common mistakes, let’s establish fundamental wiring concepts. Specifically, solar panels can connect in series, parallel, or combination configurations. Series connections increase voltage while maintaining current levels. Meanwhile, parallel connections increase current while maintaining voltage levels.
Each configuration serves different system requirements and applications. Moreover, your inverter specifications determine which arrangement works best. Additionally, environmental factors like shading affect different configurations uniquely. Clean wiring practices ensure both safety and optimal performance throughout your system’s lifetime.
Mistake #1: Improper Series vs Parallel Connections
Many DIYers confuse series and parallel wiring, creating mismatched system voltages. Consequently, this mismatch can damage inverters or charge controllers immediately. Furthermore, incorrect configurations reduce overall system efficiency significantly. Most importantly, voltage mismatches create potential fire hazards in extreme cases.
How to Fix This Mistake
First, check your inverter’s voltage input specifications carefully. Next, calculate your panel configuration to match these requirements exactly. Additionally, use a multimeter to verify actual voltage outputs before connecting. Therefore, always double-check connections against manufacturer specifications before energizing your system.
Series connections work best for higher voltage requirements and minimal shading. Meanwhile, parallel connections suit lower voltage systems with potential shading issues. However, combination wiring offers flexibility for complex installations. Moreover, proper planning prevents costly rewiring later in your project.
Mistake #2: Inadequate or Missing Fuses and Breakers
Skipping overcurrent protection represents one of the most dangerous wiring mistakes possible. Subsequently, electrical faults can cause fires, equipment damage, or personal injury. Furthermore, many local codes require proper fusing for legal installations. Additionally, insurance claims may be denied without proper safety devices.
Proper Fusing Solutions
Install fuses or breakers at every major connection point in your system. Specifically, place protection devices between panels, batteries, and inverters. Moreover, size fuses at 125% of expected current for safety margins. Therefore, calculate maximum current carefully before selecting protection devices.
DC-rated fuses differ significantly from standard AC household fuses. Additionally, solar applications require fuses designed for outdoor environments. Furthermore, breakers offer convenience but cost more than traditional fuses. However, both options provide essential protection when properly installed and sized.
Mistake #3: Using Incorrect Wire Gauges
Undersized wires create voltage drops that reduce system efficiency dramatically. Moreover, thin wires generate heat that can cause fires or melt insulation. Additionally, long wire runs require larger gauges to maintain proper voltage. Therefore, proper wire sizing ensures both safety and optimal performance.
Wire Sizing Guidelines
Calculate voltage drop using distance, current, and wire resistance values. Specifically, aim for less than 3% voltage drop in DC circuits. Furthermore, use online calculators or charts to determine proper wire gauges. Additionally, always round up to the next larger size for safety margins.
Consider temperature ratings when selecting wire for outdoor installations. Moreover, UV-resistant insulation prevents deterioration from sun exposure. Furthermore, stranded wire offers more flexibility than solid wire in most applications. Solar safety practices include regular wire inspection for damage or wear.
Mistake #4: Poor Connection Quality and Corrosion
Loose connections create resistance that generates heat and reduces efficiency. Subsequently, poor connections can arc, causing fires or equipment damage. Furthermore, outdoor connections face moisture and temperature cycling challenges. Therefore, quality connections require proper techniques and appropriate materials.
Creating Reliable Connections
Use marine-grade connectors designed for outdoor solar applications specifically. Additionally, apply dielectric grease to prevent corrosion in metal connections. Moreover, torque connections to manufacturer specifications using proper tools. Therefore, avoid relying on basic wire nuts for outdoor DC connections.
MC4 connectors provide industry-standard reliability for panel interconnections. Furthermore, crimping tools ensure proper contact pressure for long-term reliability. Additionally, heat shrink tubing adds extra protection against moisture intrusion. However, inspect all connections annually for signs of corrosion or loosening.
Mistake #5: Ignoring Grounding and Bonding Requirements
Proper grounding protects against lightning strikes and electrical faults effectively. Moreover, equipment grounding provides safety paths for fault currents. Additionally, many jurisdictions require grounding for code compliance. Therefore, understanding grounding requirements prevents safety issues and legal problems.
Implementing Proper Grounding
Connect all metal components to a common grounding system reliably. Specifically, ground panel frames, mounting hardware, and electrical enclosures together. Furthermore, use copper grounding conductors sized according to system amperage. Additionally, drive ground rods at least 8 feet into the earth.
Equipment grounding differs from system grounding in important ways. Moreover, some small systems may not require system grounding specifically. However, equipment grounding remains essential for all installations regardless of size. Therefore, consult local codes or qualified electricians when in doubt.
Prevention Strategies for Future Success
Planning prevents most wiring mistakes before they occur during installation. Additionally, creating detailed wiring diagrams helps visualize connections clearly. Furthermore, purchasing quality components costs less than replacing damaged equipment later. DIY solar basics include proper planning and preparation for successful installations.
Start with smaller systems to gain experience before tackling complex installations. Moreover, practice wiring techniques on test setups before working on actual systems. Additionally, join online communities where experienced installers share knowledge freely. Therefore, learning from others’ mistakes helps you avoid similar problems.
Tools and Materials for Quality Wiring
Invest in proper tools that ensure professional-quality connections consistently. Specifically, buy crimping tools designed for MC4 connectors and terminals. Furthermore, multimeters help verify connections before energizing dangerous circuits. Additionally, wire strippers and heat guns complete your basic toolkit.
Quality materials cost more initially but prevent expensive failures later. Moreover, marine-grade components withstand outdoor conditions much better than household alternatives. Furthermore, buying genuine parts ensures compatibility and warranty protection. Therefore, avoid cheap knockoffs that may fail prematurely or unsafely.
When to Call a Professional
Some situations require professional expertise beyond typical DIY capabilities. Specifically, grid-tie systems often require licensed electrician involvement for code compliance. Furthermore, complex battery systems with high voltages pose significant safety risks. Additionally, structural mounting may require engineering calculations for safety.
Professional inspections can catch problems before they become dangerous or expensive. Moreover, electricians understand local codes that vary significantly between jurisdictions. Furthermore, proper permits protect you legally and may be required for insurance. Therefore, consider professional help as an investment in safety and reliability.
Learning from these common wiring mistakes helps ensure your solar project succeeds safely. Moreover, proper techniques create reliable systems that perform well for decades. Therefore, take time to understand correct methods before starting your installation. Most importantly, never compromise on safety to save time or money during your project.